What factors affect the softness of non-woven fabrics, and how should these factors be controlled?
Posted by Admin | 17 Dec
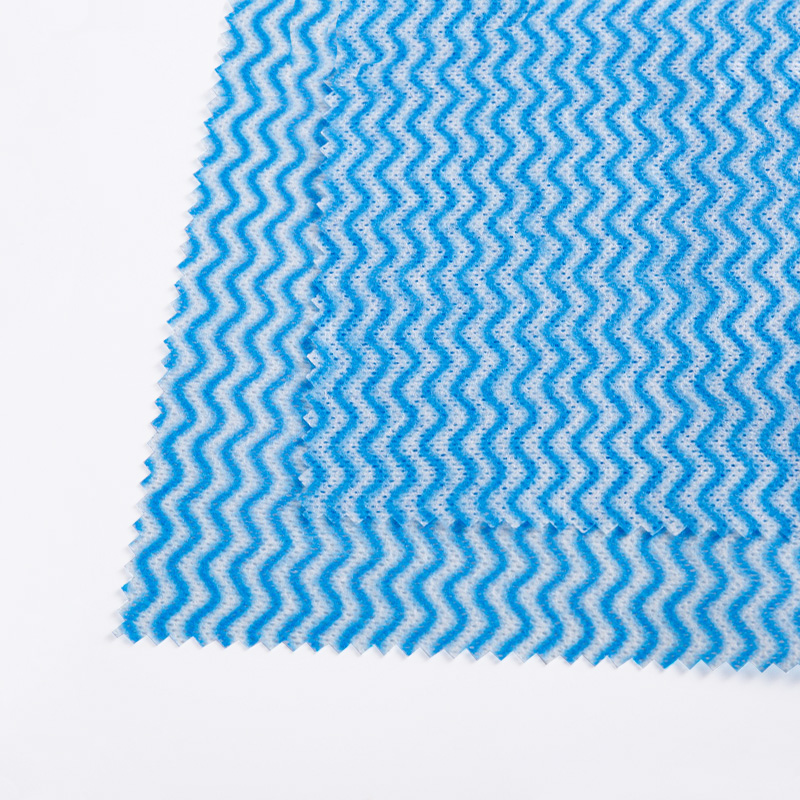
In the production process of wet wipes, there are many factors that affect the softness of non-woven fabrics. For companies like Jieli Textile Co., Ltd. that focus on the research and development and production of spunlace non-woven fabrics, it is crucial to understand and control these factors. The following is a detailed analysis of these factors and corresponding control measures:
Factors affecting the softness of non-woven fabrics
Fiber raw materials:
The softness of fiber raw materials directly affects the softness of non-woven fabrics. For example, cotton fibers have good softness and are suitable for making non-woven products with high softness requirements. Chemical fibers such as polyester are relatively stiff, but they also have unique advantages in certain application scenarios.
The fineness and length of the fiber also affect the softness of the non-woven fabric. Fibers with smaller fineness can form a finer fiber web, thereby improving the softness of the non-woven fabric.
Production process:
During the spinning process, parameters such as the orientation of the fiber will affect the softness of the non-woven fabric. Fibers with high orientation are more likely to remain in a straight state when stretched, thereby reducing the softness of the non-woven fabric.
During the web-forming process, the degree of interweaving and density of the fibers will also affect the softness of the nonwoven fabric. Nonwoven fabrics with higher interweaving and higher density tend to be stiffer.
Reinforcement method is also an important factor affecting the softness of nonwoven fabrics. Spunlace reinforcement is a relatively mild reinforcement method that can maintain the original shape and softness of the fibers.
Post-processing process:
Post-processing processes such as heat treatment, humidification, and calendering will also affect the softness of nonwoven fabrics. Appropriate heat treatment can make the fibers softer and easier to bend; humidification treatment can improve the hygroscopicity and softness of nonwoven fabrics.
Calendering treatment may improve the compactness and hardness of nonwoven fabrics by compressing the gaps between fibers.
Control measures
Optimize fiber raw materials:
Select appropriate fiber raw materials according to product requirements. For products with high softness requirements, cotton fibers and other raw materials with good softness can be given priority.
The softness and comfort of nonwoven fabrics can be improved by blending different fiber raw materials. For example, blending cotton fibers with polyester fibers in proportion can improve softness while maintaining a certain strength.
Improve production process:
Optimize spinning process parameters, such as reducing the orientation of fibers, to improve the softness of non-woven fabrics.
Adjust web forming process parameters, such as reducing the degree of interweaving and density of fibers, to form softer non-woven fabrics.
Use advanced spunlace reinforcement technology to maintain the original shape and softness of fibers.
Optimize post-processing process:
Select appropriate post-processing process parameters according to product requirements. For example, for products that need to improve softness, the number and time of humidification treatment can be appropriately increased.
Pay attention to controlling parameters such as pressure and temperature of calendering treatment to avoid over-compression of the gaps between fibers, which will cause the non-woven fabric to become hard.
For Jieli Textile Co., Ltd., its advanced imported semi-cross spunlace non-woven fabric production line and annual production capacity of up to 10,000 tons provide strong guarantees for the production of high-quality non-woven fabrics with moderate softness. By continuously optimizing the control measures of key factors such as fiber raw materials, production processes and post-processing processes, Jieli Textile Co., Ltd. can continue to provide customers with spunlace non-woven products that meet their softness needs.
+86-18058809000
+86-571 86218111



 English
English 中文简体
中文简体